Products and systems for generation Z in reduced carbon buildings
[edit] Introduction
In September 2015, BSRIA launched the white paper ‘Products and Systems for Generation Z in Reduced Carbon Buildings’, asking: what products and systems will be used in reduced carbon buildings in the future by the ‘smart’ generation?
The paper was developed for BSRIA’s Diamond Group Forum, a BSRIA network of senior executives. It was written by Jeremy Towler, Senior Manager, Energy & Smart Technologies, BSRIA Worldwide Market Intelligence, from data collected at the ISH exhibition in Frankfurt in March 2015.
The paper considers how the value of buildings can be improved to raise productivity and wellbeing for occupiers and at the same time generate new revenue streams for suppliers.
It examines:
- What will be the expectations of Generation Z – the ‘smart’ generation?
- What does our industry need to do to deliver these expectations and to achieve reduced CO2 targets over the next 10 years?
- What products and services will be required to achieve these objectives?’
Sometimes described as the ‘first tribe of true digital natives’ or ‘screenagers’, Generation Z (born from the mid-1990s to the present day) are characterised as smarter and more prudent than their Generation Y predecessors. They are empowered, have more job choices, seek freedom of movement and flexible working policies. They are the ‘see it – want it’, ‘touch it – get it now’ generation. When it comes to heating and cooling, unlike traditional systems, they expect them to just work, without any effort on their part.
[edit] What will be the expectations of Generation Z – the ‘smart’ generation?
When asked about expectations for buildings, Generation Z want devices that are aesthetically pleasing. They want to know immediately when there is something wrong in a building and, ideally, have the problem fixed immediately. They also want choice and it will be important for them to be able to choose their providers based on advice and transparency over the cost of products and services.
Regarding technology, they want simplified, flexible products, which are easily manageable because they themselves lack the skills to get involved in the detail. In short, they want passive system management.
[edit] What does our industry need to do to deliver these expectations and to achieve reduced CO2 targets over the next 10 years?
Julia Evans, Chief Executive at BSRIA, said: “Generation Z has also been characterised as the ‘sharing not the owning generation’. Therefore, there will need to be more options for renting and leasing rather than buying, due to higher capital costs. In relation to an uncertain energy future, Generation Z can see the immediate benefit of recycling.
“This generation has requested to ‘keep it simple’ and our industry needs to offer intelligent solutions that are more modular as well as being capable of being interconnected into a system to provide a global view. Therefore, products must standardise on how they communicate information between themselves. The intelligence should be built in to the controls and software.”
[edit] What products and services will be required to achieve these objectives?
Julia Evans said: “There was a general consensus that hybrid technologies would become dominant. Generation Z seem much happier to buy a service than own a product. This includes buying a solution to solve an energy-related problem, rather than the tangible product itself. Suppliers will, therefore, have to change their ‘modus-operandi’ to accommodate this stance.
“It also was found that there is a need for smarter, more connected products which are simple for both contractors and end-users. Generation Z will want the latest technology, with quick, tangible results but with little or no additional costs. There should be a focus on service – it is big business!”
--BSRIA
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Twas the site before Christmas...
A rhyme for the industry and a thankyou to our supporters.
Plumbing and heating systems in schools
New apprentice pay rates coming into effect in the new year
Addressing the impact of recent national minimum wage changes.
EBSSA support for the new industry competence structure
The Engineering and Building Services Skills Authority, in working group 2.
Notes from BSRIA Sustainable Futures briefing
From carbon down to the all important customer: Redefining Retrofit for Net Zero Living.
Principal Designer: A New Opportunity for Architects
ACA launches a Principal Designer Register for architects.
A new government plan for housing and nature recovery
Exploring a new housing and infrastructure nature recovery framework.
Leveraging technology to enhance prospects for students
A case study on the significance of the Autodesk Revit certification.
Fundamental Review of Building Regulations Guidance
Announced during commons debate on the Grenfell Inquiry Phase 2 report.
CIAT responds to the updated National Planning Policy Framework
With key changes in the revised NPPF outlined.
Councils and communities highlighted for delivery of common-sense housing in planning overhaul
As government follows up with mandatory housing targets.
CIOB photographic competition final images revealed
Art of Building produces stunning images for another year.
HSE prosecutes company for putting workers at risk
Roofing company fined and its director sentenced.
Strategic restructure to transform industry competence
EBSSA becomes part of a new industry competence structure.
Major overhaul of planning committees proposed by government
Planning decisions set to be fast-tracked to tackle the housing crisis.
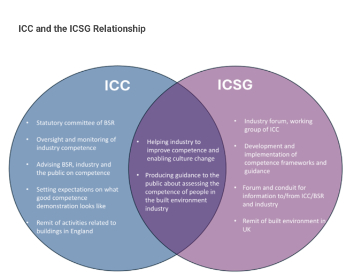
Industry Competence Steering Group restructure
ICSG transitions to the Industry Competence Committee (ICC) under the Building Safety Regulator (BSR).
Principal Contractor Competency Certification Scheme
CIOB PCCCS competence framework for Principal Contractors.
The CIAT Principal Designer register
Issues explained via a series of FAQs.